Hernias are a common medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While they may seem like a relatively minor issue, hernias can cause significant discomfort and, if left untreated, potentially serious complications. To make informed decisions about hernia management, it’s crucial to understand the different types of hernias, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of hernias, providing you with the knowledge you need to navigate this health issue effectively.
What Is a Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue pushes through a weak spot or opening in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This can result in a visible bulge or lump, and it may cause discomfort or pain. Hernias can develop in various parts of the body, each with its own unique characteristics.
Types of Hernias
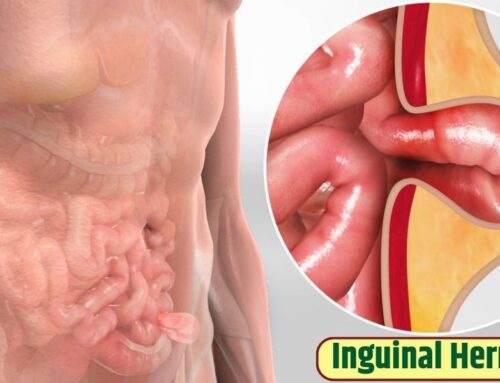
- Inguinal Hernia:
Inguinal hernias are the most common type and occur in the groin area. They are more common in men than women and can be further categorized as direct or indirect. Indirect inguinal hernias are congenital and occur due to a weakness in the abdominal wall. Direct inguinal hernias, on the other hand, are typically acquired over time due to strain and muscle weakening.
- Femoral Hernia:
Femoral hernias are less common and mostly affect women. They appear in the upper thigh, near the groin crease, and can sometimes be mistaken for inguinal hernias. Due to their location, femoral hernias can be more prone to complications, making prompt medical attention crucial.
- Umbilical Hernia:
Umbilical hernias occur when a part of the intestine or fatty tissue pushes through the abdominal wall near the navel. They are more common in infants but can also affect adults, especially those who are overweight or have had multiple pregnancies.
- Incisional Hernia:
Incisional hernias develop at the site of a previous abdominal surgery. They occur when the muscles or tissues around the surgical incision weaken, allowing organs or tissues to protrude. Obesity and improper wound care are risk factors for incisional hernias.
- Hiatal Hernia:
Hiatal hernias are unique as they occur in the upper part of the stomach, where it meets the diaphragm. They can lead to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and often manifest as heartburn or chest pain.
- Epigastric Hernia:
Epigastric hernias occur in the upper abdomen, between the breastbone and the navel. They are typically composed of fatty tissue and can cause discomfort but are not always painful.
- Spigelian Hernia:
Spigelian hernias are rare and develop along the sides of the abdominal wall. They often present as a painful lump and require surgical repair.
Symptoms and Complications
Hernias may present with various symptoms, including pain or discomfort, a visible bulge or lump, and a dragging sensation in the affected area. While some hernias are not immediately life-threatening, they can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
These complications may include strangulation, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off, leading to tissue damage or death. To prevent such complications, it’s crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a hernia.
Treatment Options
The treatment of a hernia typically involves surgical intervention, although watchful waiting may be recommended in certain cases, such as with small umbilical hernias in infants. Surgical approaches include open surgery and minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures. The choice of surgery depends on the type and size of the hernia, as well as individual patient factors.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of hernias, their causes, symptoms, and potential complications is essential for making informed decisions about your health. If you suspect you have a hernia or have been diagnosed with one, consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.
Early intervention and appropriate treatment can help alleviate discomfort and prevent serious complications, allowing you to lead a healthier and more comfortable life. Remember that your healthcare provider is your best resource for addressing hernias and ensuring your well-being.